

In contrast, distant thunder rumble and are more bass, thanks to the low frequencies with long wavelengths are able to evade obstacles and travel further. The sound of thunder in the distance makes it possible to distinguish the distant ones from the closer ones because the latter are perceived crisp and dry, more like clicking and less booming, since the high frequencies (those of the highest sounds) are still present. Sound reflects off walls quite well as well, so both properties combine to make sound bend corners quite well. It is because they have wavelengths longer than the acute ones, more or less the dimensions of doors and windows, so they have no problem in being diffracted in them, see the following figure.ĭiffraction also allows people's voices to be heard before seeing them and bumping into them around the corner, as this is the obstacle that diffracts the waves.

When you are in a room adjacent to another where music is playing, lower tones are heard better.

One person can talk to another even if there is a room in between and we can hear music and voices coming from other places, since the sound wavelengths are of comparable size or greater than everyday objects. The other two characteristic properties are interference and polarization, with refraction and reflection equally applicable to particles of matter. The jet of marbles will continue to move in a straight line, instead of immediately dispersing throughout the available space, as waves do.Definitely the material particles at the macroscopic level do not experience diffraction, but the electrons, even having mass, can.įor this reason, all physical phenomena that are manifested through diffraction must be of the wave type. Imagine for a moment that instead of water it was a stream of marbles that passed through the openings.
#Diffraction of sound waves windows
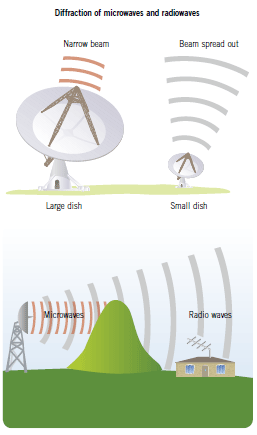
The waves will manage to avoid the opening and continue on their way, but their shape will have changed according to the size of the slit, to unfold once it is past it.įor example, the tiny particles in the atmosphere act as obstacles for light to diffract, causing rings to be seen around very luminous objects such as light and the sun.įor sound waves, on the other hand, diffraction is facilitated, since their wavelength is of the order of meters, so openings the size of doors and windows are enough for it to occur.ĭiffraction is a unique property of waves. When the source is activated, a wave front is generated that moves in the tray and to which an obstacle can be interposed with an opening in the middle. The source can be as simple as a vibrating metal band. This property is easy to verify using a wave bucket, which consists of a tray filled with water and a source that generates the waves placed at one end. In doing so, they are distorted and the smaller the aperture through which they pass, the greater that distortion. The diffraction sound It is the property of waves to flex at the edges of obstacles or openings equal to or less than their wavelength and continue to propagate.
Video: Sound: Diffraction and Interference | Physics in Motion Content


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
